Source:
Yoruk, I., Hsu, J.-H., & Lee, Z. W. Y. (2024). Consumer forgiveness: A literature review and research agenda. Psychology & Marketing, 1–25. https://doi.org/10.1002/mar.22138
In the latest episode of Marketing Science Lab, we take a deep dive into groundbreaking research on consumer forgiveness. The study, published in Psychology & Marketing in 2024, synthesizes findings from 89 articles to provide a comprehensive understanding of how brands can rebuild relationships after negative events. This research is crucial for marketers navigating an increasingly complex and transparent marketplace.
Understanding the Consumer Forgiveness Process
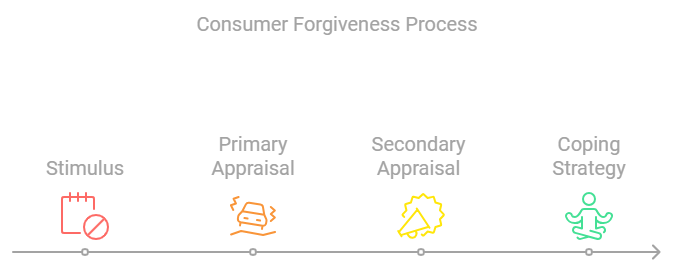
At the heart of the research is a framework that views consumer forgiveness as a coping process. This process involves several key stages:
Stimulus: A negative marketing event occurs, such as a product failure, service mishap, or brand transgression.
Primary Appraisal: Consumers evaluate the severity and impact of the event, assessing the brand's responsibility. Key factors include perceived severity, intent, stability, and controllability.
Secondary Appraisal: Consumers evaluate the brand's recovery efforts and assess available resources to cope with the situation. Perceived justice (distributive, procedural, interactional) and trust repair play crucial roles here.
Coping Strategy: Based on these appraisals, consumers choose to either forgive the brand, avoid it, or seek revenge/retaliate.
This framework provides marketers with a roadmap for understanding the psychological journey consumers undergo when deciding whether to forgive a brand transgression.
Key Factors Influencing Consumer Forgiveness
The research highlights several critical factors that influence a consumer's likelihood to forgive:
Attribution: How consumers attribute the cause of a negative event significantly impacts their forgiveness. Events perceived as unintentional, unstable, and uncontrollable are more likely to be forgiven.
Justice Perception: Consumers are more likely to forgive when they perceive the brand's recovery efforts as fair and just. This includes distributive justice (fair compensation), procedural justice (fair processes), and interactional justice (respectful communication).
Emotional Transformation: Forgiveness involves transitioning from negative emotions to more positive or neutral states. Brands that facilitate this emotional shift are more likely to be forgiven.
Individual Differences: Factors like personality traits, cultural background, and past experiences with the brand can influence a consumer's propensity to forgive.
Relationship Strength: Generally, stronger pre-existing relationships with a brand increase the likelihood of forgiveness, but this can backfire if consumers feel a sense of betrayal.
Actionable Strategies for Marketers
Based on the research findings, we can extract several actionable strategies for marketers facing brand crises:
Prioritize Transparency: Be upfront about what happened and why to reduce negative attributions and increase perceived controllability.
Tailor Recovery Efforts: Consider the nature of the transgression, the strength of the pre-existing relationship, and individual consumer characteristics when crafting recovery strategies.
Address All Justice Dimensions: Ensure recovery efforts encompass distributive (fair compensation), procedural (clear resolution processes), and interactional (empathetic communication) justice.
Facilitate Emotional Transformation: Design recovery experiences that help consumers move from negative emotions to more positive states.
Leverage Brand Communities: Nurture positive sentiment within brand communities, as this can influence individual consumers' forgiveness processes.
Invest in Relationship Building: Continuously invest in building genuine connections with customers to create a buffer during negative events.
Consider Cultural Factors: Be aware of how cultural differences might impact forgiveness processes, especially for global brands.
The Role of AI and Social Media in Consumer Forgiveness
The research also highlights emerging areas that marketers need to consider:
AI and Forgiveness: As more customer interactions become automated, understanding how consumers attribute blame and forgive AI-driven service failures is crucial.
Social Climate Impact: Social media firestorms and online sentiment can significantly influence individual forgiveness processes. Real-time monitoring and rapid response plans are essential.
Self-Concept Maintenance: Consider how forgiving a brand might align with a consumer's self-image or values, and how this can be leveraged in recovery strategies.
By understanding these complex dynamics, marketers can develop more effective strategies for rebuilding trust and fostering long-term customer loyalty, even in the face of brand transgressions.
Interactive Quizlet: https://quizlet.com/study-guides/understanding-consumer-forgiveness-in-brand-recovery-51604789-fd6d-4191-b462-2329c008108a?i=3i62em&x=13qt













Share this post